The UL standards, developed by Underwriters Laboratories, provide essential benchmarks for product safety and certification. The Underwriters Laboratories itself is a renowned global safety certification company that applies strict scientific safety standards to promote safe living and working conditions. Their standards guarantee that products meet high safety and reliability requirements in many industries and product types.
Our daily lives are closely connected with the standards of a multitude of organizations. New standards emerge every day. They cover everything from the food we buy in stores to the clothes we wear. Nevertheless, international standards exert far broader influence than these everyday items. Material testing is one of the most critical areas affected by these standards. As well as ensuring the quality of products, these standards also guarantee public safety and environmental protection.
Throughout this article, we will explore the role of UL standards in material testing. Our discussion will focus on UL standards and their necessity in modern society. Moreover, we will examine examples of these standards, their application areas, and their purposes. The discussion will also cover the tools that comply with these standards, demonstrating their capabilities and intended uses. With this insight, we hope to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of UL standards in our daily lives.
Underwriters Laboratories: An Innovator in Safety Science

Let’s start with the basics. Underwriters Laboratories, or UL, is an institution specializing in safety science and certification. Since its founding in 1894 by William Henry Merrill, UL has expanded its scope and services significantly. Merrill began his career as an electrical inspector at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, which eventually led to the creation of UL.
As early as 1907, UL conducted groundbreaking tests on roofing materials and building columns. UL’s testing methods were radically altered during this period, including the development of a U.S. standard for the Standard Time-Temperature Curve in 1920. As UL expanded beyond product testing, it tested airplanes in the 1920s and helped create the Civil Aeronautics Board in 1923.
In the 20th century, UL expanded its testing capabilities and scope. It tested and developed safety measures for many applications during World War II. Since the postwar era, UL has intensified its focus on consumer electronics, office machines, and emerging technologies. By the 1950s, UL was testing television safety, mainframe computers, and early consumer electronics like the Xerox 914 copier.
With time, UL’s focus has expanded to include a broad range of safety concerns. Among them are hazardous substances, water quality, food safety, environmental sustainability, and performance testing. In 2012, UL changed its structure to become the parent company of UL LLC, which took over the product testing and certification business in the United States.
UL’s extensive range of standards reflects its growth and diversification. Among the products and components covered by these standards are electrical equipment, life safety devices, building products, industrial control equipment, plastic materials, wire and cable, and even photovoltaic systems.
Since its inception, UL has partnered with certifiers in many countries and opened inspection offices there. U.S. safety standards were met through this global expansion. In recent years, UL has established subsidiaries and gotten accreditation in various countries to facilitate international product certification.
Paving the Way in Different Industries
UL standards extend far beyond the scope of material testing, covering an extensive number of industries. This widespread application illustrates how deeply these standards have become integrated into the global fabric of safety and quality. To understand the global influence and reach of UL standards, let’s look at some of these diverse industries:
Automotive and the Mobility Industry
UL standards guide manufacturers through complex safety, security, quality, and performance challenges in the automotive and mobility industries. The need for these standards is especially critical given the industry’s rapid evolution, driven by advancements in autonomous technology, connectivity, electrification, and shared mobility.
From automotive and commercial vehicles to e-mobility and micromobility, UL is involved in multiple facets of the industry. As one example, UL 2580, a standard for Batteries for Use in Electric Vehicles, ensures that batteries meet rigorous safety and performance standards. A battery-electric vehicle (BEV) and a plug-in hybrid vehicle (PHEV) are both integral components of testing under this standard.
UL’s comprehensive solutions are beneficial to the e-mobility segment, which includes electric vehicles. In addition to fire safety, electric shock prevention, functional safety, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) immunity, these solutions focus on product safety and performance across the e-mobility value chain. UL also provides extensive research, testing, certification, and compliance services that help manufacturers understand and mitigate safety risks associated with their innovative battery and charging technologies.
Furthermore, UL standards specialize in batteries and energy storage. The organization provides automotive innovation advisory, testing, inspection, certification, and training services to ensure that advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and novel micromobility technologies adhere to the highest safety standards. Manufacturing companies need this support as they deal with an increasingly complex set of industry standards and best practices.
Buildings and Construction
In the building and construction industry, these standards are designed to cover fire safety, electrical systems, building materials and structural integrity.
For instance, UL 10A addresses the fire-resistance capabilities of Tin-Clad Fire Doors. In an emergency, this standard is crucial for making sure that fire doors provide effective protection and safe egress routes in buildings during fire conditions.
A similar standard, UL 20, covers electrical switches used in buildings and ensures their safety and reliability. Several aspects of this standard make sure the switch is safe for long-term use in residential and commercial buildings, including construction, performance under normal and abnormal conditions, and endurance.
UL’s contribution to architecture, engineering, and construction industry extends to testing, inspection, and compliance (TIC) services. In addition to planning and managing building and infrastructure projects, these services guarantee compliance with safety and environmental regulations. In this sector, UL’s comprehensive approach supports industry professionals in addressing significant challenges like safety, sustainability, compliance, and quality, enhancing overall performance and reliability.
Technology and Electronics

UL standards are comprehensive in the technology and electronics industry, covering everything from consumer electronics to complex IT equipment, which is why they are so popular.
UL 60950, the standard for Information Technology Equipment, is a prime example. Among other things, it addresses the safety of electrical and electronic devices in different environments, such as offices and homes. This standard is essential for devices like computers, servers, and network infrastructure equipment, which guarantees they are built to withstand common electrical risks and operate safely under normal conditions.
UL 62368 is another important standard for audio/video and communication equipment. It was designed for the modern era of electronic devices when the lines between different types of technology are increasingly blurred. TVs, audio systems, and complex networking devices are all subject to this rigorous safety standard.
In addition to these, UL provides services for EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) and wireless testing, essential for making sure that electronic devices do not interfere with each other’s operations and maintain performance standards. This includes testing for compliance with regulatory bodies like the FCC in the USA and similar agencies worldwide.
UL standards also specialize in Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) testing. The SAR testing of mobile phones makes sure they meet global safety standards for human exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields.
Furthermore, UL offers testing and certification services for newer technologies such as Augmented, Virtual, and Mixed Reality. Through the upcoming UL 8400 standard, UL is evaluating the safety risks associated with these innovative products.
Healthcare and the Life Sciences
The last industry on our list is healthcare and life sciences. UL standards cover a diverse range of products and applications in the healthcare and life sciences industries. They address the challenges unique to this highly regulated sector, and they are designed to meet these challenges.
UL 2900, for example, has a significant role to play in software cybersecurity in network-connected products. A medical device, an accessory, an in vitro diagnostic device, health information technology, and a wellness device are covered by this standard. An era where digital health technologies are becoming more prevalent demands that healthcare systems offer security and safety to networked components.
There are also notable UL standards in this industry, such as UL 416 for Refrigerated Medical Equipment, which covers devices like thermal and oxygen therapy devices. Another important standard is UL 1637 for Home Health Care Signaling Equipment, which ensures the reliability of home healthcare systems required for patient monitoring and emergency communications.
In addition to these, UL 1069 for Hospital Signaling and Nurse Call Equipment and UL 2560 for Emergency Call Systems in Assisted Living and Independent Living Facilities are vital for communication systems in healthcare settings. These standards make sure that such systems function effectively, facilitating timely responses in care facilities.
As well as testing and certifying pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and health and wellness retail, UL is involved in other aspects of healthcare and life sciences. UL offers comprehensive services in this sector, including sterility testing, antimicrobial preservation, microbial enumeration, and bacterial endotoxins, as well as tests for particulate contamination in injections and ophthalmic solutions.
UL Standards for Material Testing

As previously discussed, UL standards, beyond their primary industry applications, play an extraordinarily influential function in material testing. Using these tests guarantees the safety and quality of a wide array of materials. Plastics, engineered materials, and recycled plastics are among the materials that these standards apply to.
As part of its testing process for plastics, UL conducts mechanical tests such as tensile strength, bending resistance, and impact resistance. The tests are crucial in assessing how plastic materials perform under stress, with standards such as UL 746A and ASTM D638 being used to ensure the reliability and safety of plastic materials. An important parameter derived from these tests is the elasticity modulus (E modulus), which is used to compare materials and evaluate their stiffness.
UL standards are also rigorously applied to recycled plastics. In electrical equipment, for example, UL 746S evaluates sustainable polymeric materials. With this standard recycled plastics have the same safety ratings as virgin resins within the same product category. The certification process for recycled plastics includes infrared analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, differential scanning calorimetry, and flammability tests. Tests such as these verify that recycled materials meet safety and quality standards.
As a result of UL’s testing and certification processes, manufacturers can demonstrate that their materials are fit for their intended applications, as well as demonstrate compliance with safety standards. With this comprehensive approach to material testing, UL is advancing public safety and quality assurance in a number of industries.
Common UL Standards Used in Material Testing
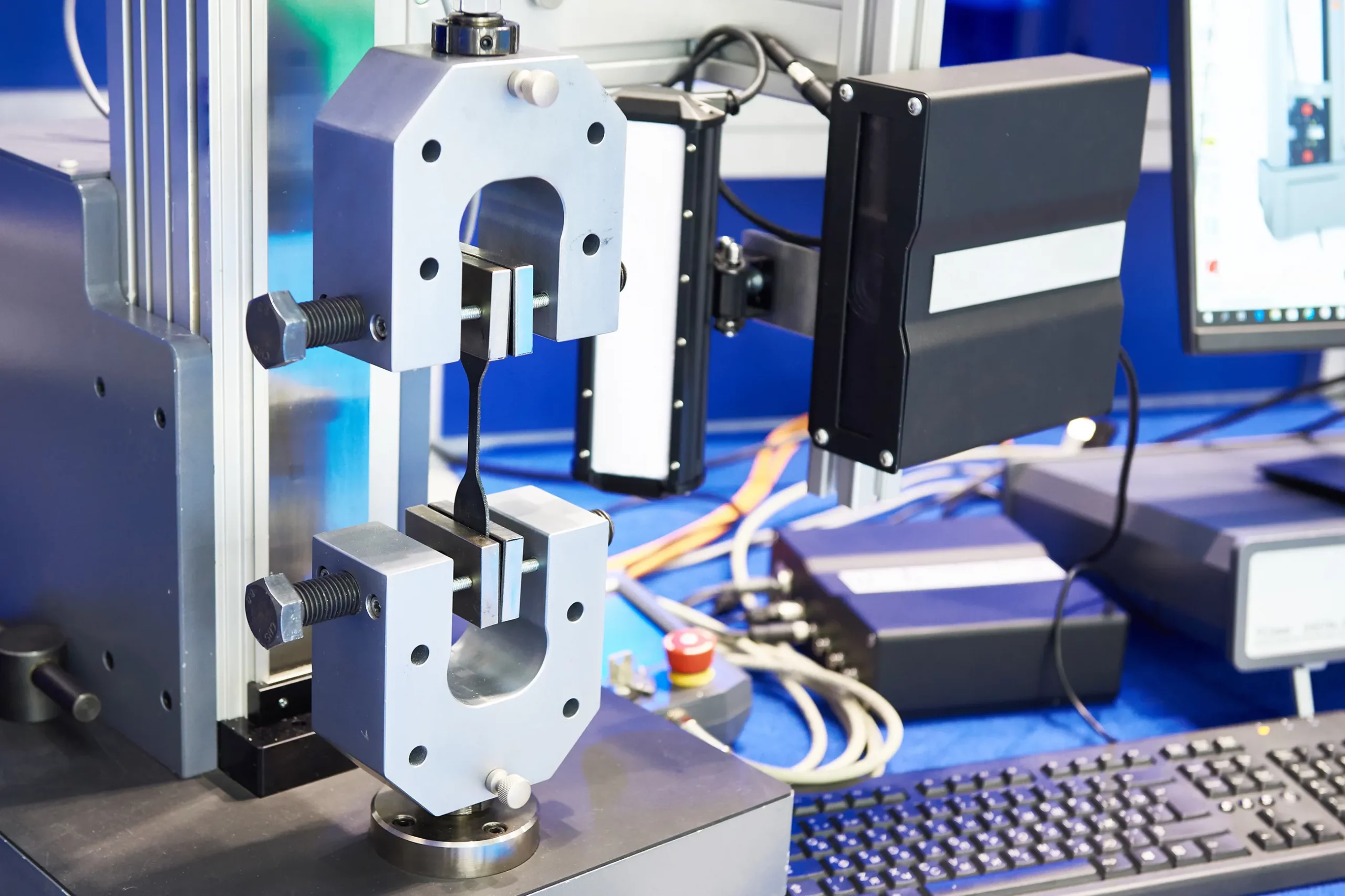

In addition to the specialized UL standards we have already discussed, there are other commonly used standards. Among them are standards such as those listed in the following list, which typically pertain to conduits:
Standard UL 1 for Flexible Metal Conduits
Let’s begin with UL 1, which is a standard specifically for flexible metal conduits. As a metal raceway for wires and cables, this standard certifies the safety and reliability of flexible conduits made from aluminum, steel, and stainless steel materials. It aligns with the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70, highlighting the need to ensure compliance with national safety standards.
Following the 2023 NEC, UL’s latest revision of UL 1 includes updates for Stainless Steel Flexible Metal Conduit (SS FMC) as an Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC). The purpose of this standard is to provide guidelines to manufacturers and users of flexible conduits so that electrical wiring is effectively protected.
UL 6 Standard for Electrical Rigid Metal Conduits
The UL 6 standard applies to Electrical Rigid Metal Conduit – Steel (ERMC-S). Conduits, elbows, couplings, and nipples made of steel are used as metal raceways for installing wires and cables. The National Electrical Code, Canadian Electrical Code, and Standard for Electrical Installations are all included in this standard.
As part of UL 6, these conduits must be equipped with corrosion-resistant exterior coatings and appropriate interior coatings. According to the latest edition of UL 6, published in 2022, references in Annex A have been updated, measurements have been corrected, and specific gravity range adjustments have been made for copper sulfate solutions. Underwriters Laboratories maintain high safety standards in line with current industry practices and technological advancements through these updates.
UL 360 for Liquid-Tight Flexible Metal Conduits
UL 360 covers the design, manufacture, testing, and certification of liquid-tight flexible metal conduits. Specifically, this standard guarantees the safety and reliability of conduits used for different purposes, especially when flexibility is needed during installation, operation, or maintenance. In addition to conduits made from steel, aluminum, brass, bronze, copper, and stainless steel, it also addresses conduits that can be used in wet, dry, or oily conditions. The UL 360 certification ensures that these conduits are constructed with a liquid-tight, nonmetallic, sunlight-resistant jacket over a flexible metal core.
It is essential for applications in which wires and cables need to be protected from vapors, liquids, or solids and may be exposed but not damaged physically. For conduits with stainless steel cores, UL 360 includes specific requirements and exemptions to verify that they meet contemporary safety and quality standards.
UL 651: The Standard for Safety in PVC Electrical Conduits
UL 651 is the next item on our list, which is a significant standard developed by Underwriters Laboratories that specifically focuses on the use of PVC electrical conduits in electrical installations. It is a category that encompasses a wide range of PVC conduits such as Schedule 40, Schedule 80, Type EB, and Type A, which are used as rigid nonmetal raceways for wires and cables in compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC), NFPA 70.
It includes parts that are used in conduit systems, including elbows, couplings, adapters, and similar fittings, which are primarily constructed from rigid PVC. Scheduling 40, Scheduling 80, and types EB and A refer to the USA trade sizes of conduits with specific thicknesses of wall and outside diameters, similar to iron pipes, that are used in USA trade.
Standard UL 797 for Electrical Metallic Tubing
UL 797 is another safety standard for the manufacture, consumption, and installation of Electrical Metallic Tubing – Steel (EMT), which is used as a metal raceway for cables and wires. According to NFPA 70, this standard is necessary to confirm that the EMT complies with the safety requirements of several electrical codes. These include the Canadian Electrical Code and NFPA 70. UL 797 certifies that EMTs are equipped with appropriate corrosion-resistant exterior and interior coatings.
Several significant changes were made to the standard in its latest revision in 2023, including introducing a range for specific gravity and adding larger trade sizes (5″ & 6″) in steel EMT as a result of the revision.
UL 1242 Standard for Steel Electrical Intermediate Metal Conduits
There is another comprehensive standard called UL 1242 that regulates steel electrical intermediate metal conduits (IMCs), as well as all its components, such as nipples, elbows, and couplings. The conduit is available in a wide range of trade sizes, from 1/2 to 4 (16 to 103), and is designed to be used as a metal raceway for wire and cable installations, as specified in The National Electrical Code (NEC), NFPA 70. The standard ensures that steel IMC is equipped with suitable levels of corrosion resistance for normally corrosive environments.
An updated version of UL 1242, updated in 2022, introduced some key changes, including developing minimum acceptable elbow dimensions and revising editorial content. As a result of these changes, UL 1242 remains up-to-date and aligned with industry practices and standards that continue to evolve.
UL 1660 Standard for Liquid-Tight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit
UL 1660 is the last standard on our list, and it pertains to liquid-tight flexible nonmetallic conduits that are flexible and nonmetallic. This standard covers a range of conduit types, such as LFNC-A (Layered), LFNC-B (Integral), and LFNC-C (Corrugated). LFNC-C is designed to be installed in a variety of environments, such as wet, dry, or oily locations, at temperatures up to 60°C (140°F). The purpose of the standard is to make sure that the conduits comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC), the Canadian Electrical Code, and the Mexican Electrical Code so that they can be used to safely house and protect electrical wiring.
The conduits specified by UL 1660 are designed to provide a safe and reliable path for electrical cables, providing them with protection from environmental factors and mechanical damage, as well. There has been a recent revision to UL 1660, with an update due in January 2023, to verify that the standard remains relevant and effective in addressing the current safety requirements in the electrical industry.
DWT-1800: The Ultimate Tool for UL Standards Compliance
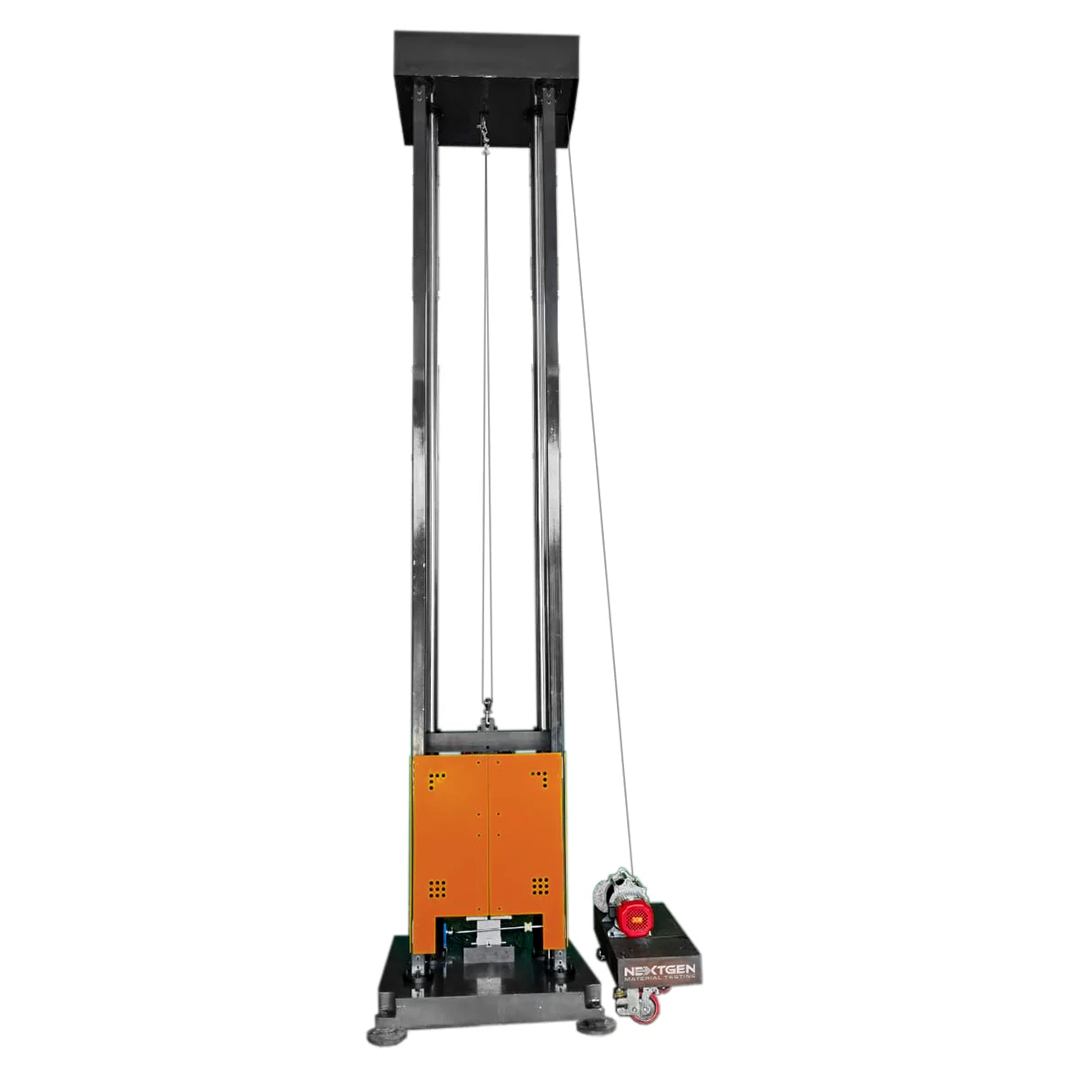

We have some exciting news for you if you are looking for advanced equipment that can handle UL standards easily. We would like to introduce you to our DWT-1800, the ideal choice for material testing, fully compliant and specifically designed to work with UL standards such as UL651, UL1, UL360, UL1660, UL797, UL6, UL1242, in addition to UL1569, UL2239, UL514C, and UL514D. As a versatile machine, it is particularly well suited for the testing requirements of many different industries that have rigorous testing requirements.
As one of the main features of the DWT-1800, we can point out that it can exert an impact energy of 1800J, can lift a maximum weight of 600 lbs, and has a maximum lifting height of 3.35 meters. A precision-engineered machine built with a sturdy guide rail, a strong base, a sturdy anvil, a hammer, and a lifting mechanism. The guide rail makes sure that the hammer falls exactly in line with the guide rail and in a parallel manner. There are a number of safety mechanisms built into the equipment to ensure the operator’s safety, including a manual iron block safety mechanism, and a device to prevent the scatter of debris during specimen breakage.
DWT-1800 is also equipped with a microcomputer-controlled impact energy pre-set system, enabling precise pre-setting of hammer mass and test energy, as well as automatic hammer lift to the height that is required. It is also supported by many safety protection devices that are monitored throughout the testing process. With its electric lifting mechanism, the DWT-1800 is a reliable, efficient and reliable solution to impact testing across a variety of industrial applications, thanks to its enhanced stability and ease of maintenance.
To Sum Up: UL Standards in Material Testing
Our comprehensive overview of the UL standards in different industries and their impact on a wide range of industries has discussed how these standards guarantee safety, quality, and reliability across a wide range of industries. From the automotive and mobility industry, where standards like UL 2580 increase battery safety, to the building and construction sector with UL 10A and UL 20 providing fire and electrical safety, UL standards are fundamental in establishing safety benchmarks.
UL 60950, UL 62368, and UL 2900 are some of the many standards that play key roles in ensuring the safety of products and protecting sensitive medical data across technology, electronics, healthcare, and life sciences. In addition, we have taken a closer look at specific UL standards, including UL 1, UL 6, UL 1242, and UL 1660, each of which are crucial in their respective areas of application, such as flexible metal conduits, electrical steel conduits, and liquid-tight nonmetallic conduits.
NextGen Material Testing Inc. can help you comply with these standards in material testing. The equipment we offer is specially designed for UL standards and we offer expert guidance. To meet your specific testing requirements, our team provides the necessary knowledge and customized solutions. You can contact us or request a quote online at any time. Our top-of-the-line equipment and expertise will help you achieve excellence in material testing.