Material corrosion is a natural process that deteriorates metals and other materials due to chemical reactions with their environment. This leads to large material losses and failures. This phenomenon is primarily driven by electrochemical processes, occurring when materials react with elements such as oxygen and water. Corrosion risk includes weakened structural integrity, potential failures in critical applications, and considerable economic costs due to repairs or replacements.
While a number of methods are available to test materials for corrosion resistance, finding reliable testers remains a challenge. Hence, NextGen have introduced the Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt, a precision and dependable tool engineered to deliver accurate and consistent results. This tester is specifically designed to assess how different coatings and materials withstand harsh corrosive environments, thereby verifying the durability and longevity of the product’s materials.
The purpose of this article is to explore the unique features and capabilities of our Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt and understand why tools like this are needed in highly critical corrosion resistance testing. We will discuss the robust standards it complies with and the array of materials that can benefit from its testing methods. By the end of this article, readers will gain a thorough understanding of how our tester can serve as a valuable tool in preventing material corrosion.
Understanding Material Corrosion Risks
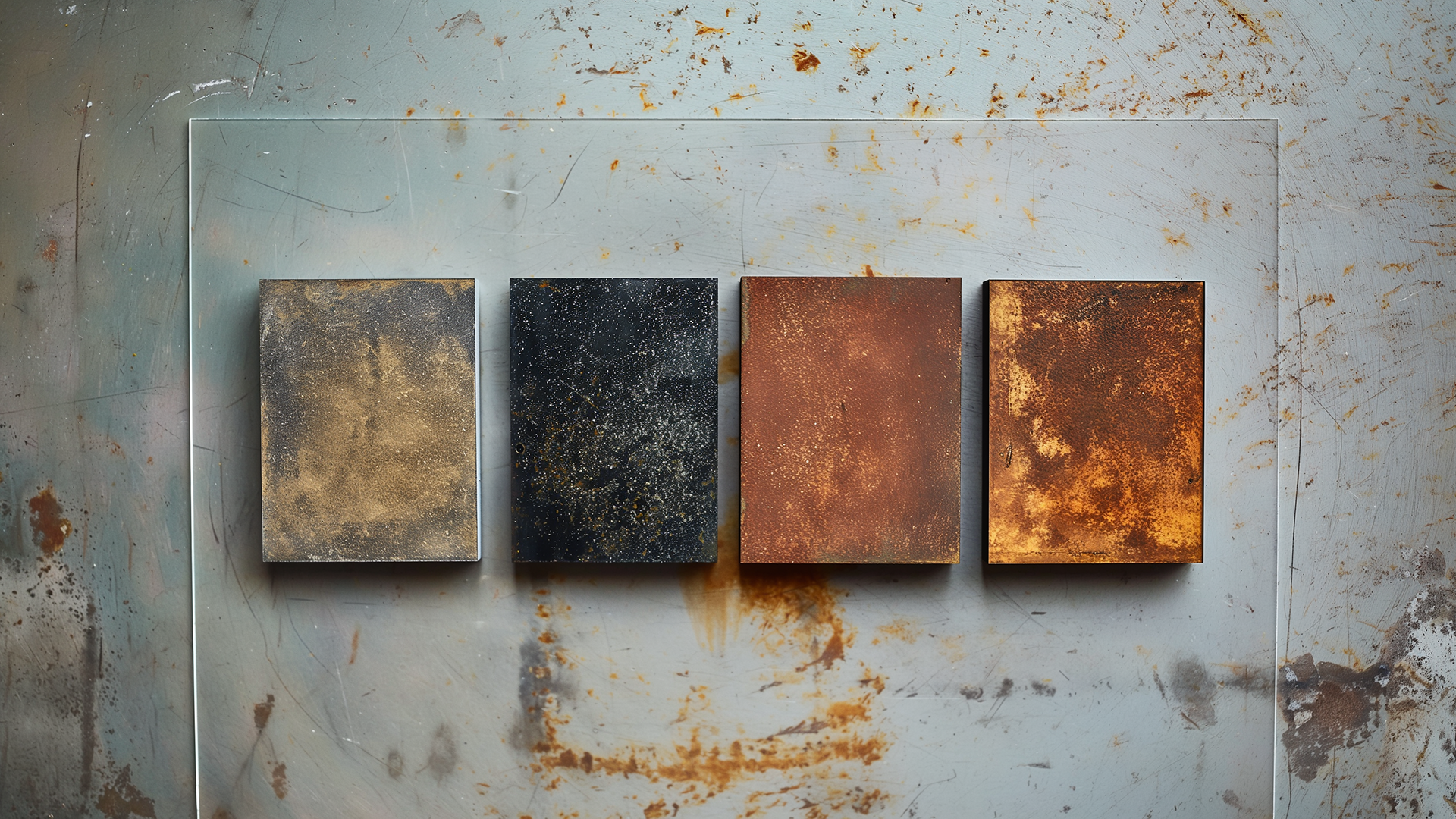
In order to gain a deeper understanding of the tester, we must first learn about the dangers and risks associated with the corrosion of the material. Material corrosion presents significant risks not only due to its financial impact, which amounts to an estimated global cost of $2.5 trillion annually but also because of the severe safety hazards it poses. Corrosion, the chemical reaction of materials with their environment, leads to the deterioration of metals and compromises the structural integrity of infrastructures. This degradation can result in potentially catastrophic structural failures, threatening safety and operational stability.
Corrosion dangers extend beyond mere structural damage. In industrial equipment, even minor corrosion can precipitate severe mechanical failures, posing immediate risks to operational safety and efficiency. These failures often result in accidents or operational downtimes, translating into significant financial losses and safety risks. Moreover, corrosion poses profound environmental and health hazards. Corroded structures can leak toxic substances into ecosystems, creating long-term health risks to humans and wildlife.
Electrical hazards of corrosion are equally concerning. Corroded metals can disrupt electrical pathways, leading to short circuits, which may cause fires or explosions, thereby endangering lives and property. Given these multifaceted risks, the use of reliable testing methods to assess corrosion resistance becomes indispensable for guaranteeing the longevity and safety of materials.

Introduction to the Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt
The Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt is the leading corrosion resistance test instrument, specifically designed to evaluate the durability of different materials in corrosive environments. This advanced testing unit is primarily used for assessing coated metallic surfaces, which has made it a key tool in industries with high demands for material longevity and coating durability.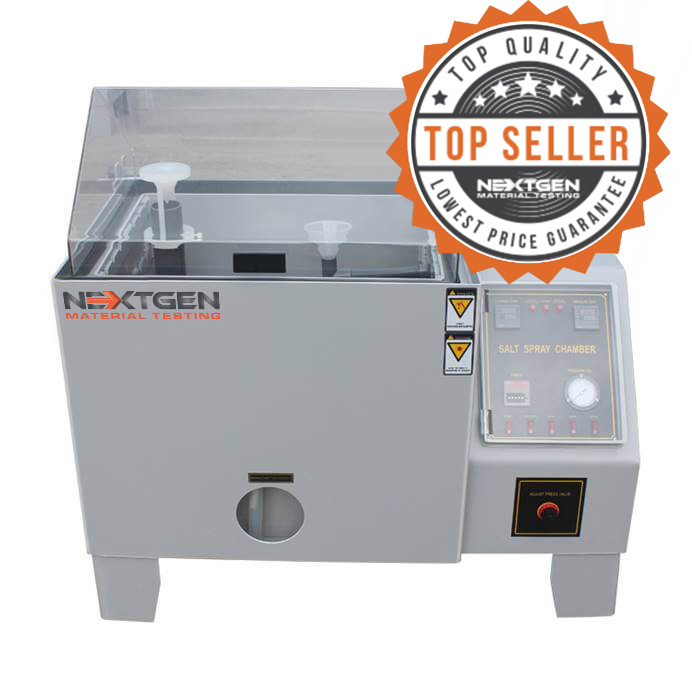 
The GenSalt tester applies a salt spray to simulate accelerated corrosion, allowing to determine the effectiveness of rust-proof treatments such as painting, anodizing, electroplating, and grease application.GenSalt’s methodology involves exposing test samples to a controlled corrosive environment, where salt spray accelerates the natural corrosion process.
This approach allows for the quick assessment of a material’s corrosion resistance, quantifying how long a sample can withstand visible corrosion. Manufacturers and engineers rely on the results of these tests to improve product formulations, develop protective coatings, and confirm material compliance with safety and quality specifications.
Unique Features of Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt
Our Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt features are designed to optimize efficiency and provide comprehensive insights into the corrosion resistance of different materials. To gain a better understanding of its features, let us take a closer look at them.
Robust Construction
 The Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt is engineered with precision based on corrosion resistance testing demands. GenSalt components are designed to enhance functionality and reliability. Starting with its construction, the GenSalt features a sturdy, impact-resistant structure made of a 5mm PVC plate that withstands temperatures up to 85°C. This material choice prevents deformation under long-term high-temperature exposure, thanks to its 15mm thick reinforced PVC material at the inner and outer edges. The resilience of these materials guarantees that the tester maintains its structural integrity over time, even under extreme conditions.
The Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt is engineered with precision based on corrosion resistance testing demands. GenSalt components are designed to enhance functionality and reliability. Starting with its construction, the GenSalt features a sturdy, impact-resistant structure made of a 5mm PVC plate that withstands temperatures up to 85°C. This material choice prevents deformation under long-term high-temperature exposure, thanks to its 15mm thick reinforced PVC material at the inner and outer edges. The resilience of these materials guarantees that the tester maintains its structural integrity over time, even under extreme conditions.
Advanced Internal Mechanisms
Internally, the GenSalt incorporates a saturated air tank made from SUS#304 stainless steel, renowned for its high-pressure tolerance and optimal insulation properties. This tank is necessary for maintaining the controlled environment necessary for accurate corrosion testing. Additionally, the sample placing anvil is crafted from an 8mm temperature-resistant ABS plate, developed specifically to support high weights.
Precision Spray System
One of the most critical components of the GenSalt is its spray nozzle, which is made from special glass material. This nozzle can be adjusted to modify both spray amount and angle. The spray amount itself is finely adjustable from 1 to 2 ml/h, aligned with industry standards which generally require 16 hours of continuous testing on average.
Innovative Features for Reliable Testing using the Salt Spray Tester
GenSalt operates on the Bernotte principle to atomize brine, providing a uniform atomization degree that prevents crystallization obstruction. This feature serves as a key to maintaining the consistency of the testing environment. It guarantees that each test meets stringent standards for reliable results. The device also features a dual pressure adjustment system. The first stage roughly adjusts to 2 kg/cm2 and includes an air filter with a drainage function, while the second stage allows for precision adjustments to 1 kg/cm2.
 Enhanced Usability and Safety
Enhanced Usability and Safety
Additional features aimed at increasing usability and reliability include a fast heating rate for maximum efficiency and a pure titanium heating tube that resists acid and alkali corrosion. The test chamber heating tank incorporates a liquid expansion safety temperature controller that ranges from 0-120°C, sourced from EGO of Italy, allowing safe operation at different levels of temperatures.
Control and Monitoring
Moreover, the GenSalt is equipped with an advanced control system featuring an LCD digital display time controller with power failure memory function, provided by Japan’s OMRON, and an accumulator to track up to 99999 hours of operation.
Operational Convenience
For operational convenience, the GenSalt includes a rocker with a light switch tested to work continuously 25,000 times, alongside an innovative water-adding system. This system features both automatic and manual watering systems, which help maintain appropriate water levels in both the pressure tank and the test chamber, protecting against water shortages and potential ultra-high temperature damage.
Defogging System
Lastly, the defogging system is a standout feature, operating both during the test process and upon shutdown to remove salt spray from the test chamber. This system helps prevent corrosion gases from damaging the chamber and other precision instruments.
Additional Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt Safety Features
The GenSalt Salt Spray Tester is equipped with advanced safety mechanisms to provide reliable operation and protect users and equipment. These safety features are carefully designed to respond to potential risks during testing procedures. Firstly, the tester includes a safety protection device that automatically turns off the power when the water level is low. This activates a safety warning light to alert the operator. Similarly, if the temperature exceeds safe operational limits, the heater power is automatically disabled to prevent overheating, with a corresponding safety warning light activation.
Moreover, GenSalt is proactive in its approach to chemical management. When the level of the reagent, specifically salt, drops below the required threshold, the system lights up a safety warning but also triggers an alarm to call for immediate attention. Additionally, the tester incorporates a leakage protection function, which is vital for preventing personal injury and instrument failure.
Standards Compliance of the Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt
In the realm of corrosion testing, the Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt complies with two primary standards: ISO 9227 and ASTM B117. These standards are crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable testing outcomes. Let’s explore each of these standards more closely.
ISO 9227 Standard
ISO 9227:2022 describes tests designed to assess metallic materials’ corrosion resistance, with or without permanent or temporary corrosion protection. It specifies the equipment, reagents, and procedures for conducting neutral salt spray (NSS), acetic acid salt spray (AASS), and copper-accelerated acetic acid salt spray (CASS) tests. These tests are invaluable for detecting discontinuities such as pores and other defects in metallic, organic, anodic oxide, and conversion coatings.
The standard provides a thorough method for evaluating the corrosivity of the test cabinet environment. However, it does not dictate the dimensions or types of test specimens, nor the exposure periods for specific products. This flexibility allows the standard to be adapted according to the specific needs of the products being tested, as detailed in their respective specifications. Importantly, ISO 9227 is not intended for comparative testing to rank materials or predict long-term corrosion resistance.
ASTM B117 Standard
ASTM B117-19 establishes practices for operating salt spray (fog) tools and creates a controlled corrosive environment used to produce relative corrosion resistance information for specimens of metals and coated metals. This practice does not prescribe specific test specimen details or exposure periods, which should be customized to the particular needs of the tested products.
It’s important to understand that while salt spray tests are an excellent tool for simulating and accelerating real-world corrosive conditions, results from these tests should not be used in isolation to predict real-world corrosion resistance. Correlations between accelerated testing and actual field performance can vary, and thus, these tests are often one part of a broader suite of corrosion tests.
Materials Tested for Corrosion Resistance Using GenSalt
Through simulations of accelerated corrosive conditions, GenSalt helps manufacturers determine how well paints, anodized metals, electroplated coatings, and grease treatments will hold up in real-world situations. Besides ensuring durable products, this testing confirms that the materials can withstand harsh environments. Let us show you more detailed materials that need to be tested for corrosion using salt spray testers like our GenSalt.
Rust-Proof Paint
Rust-proof painting involves applying specific paint formulations to prevent metal corrosion. These paints typically contain corrosion inhibitors that form a protective barrier, shielding the underlying metal from moisture, salts, and other corrosive elements.
Rust-proof paints are commonly used in industries such as automotive, construction, and marine, where metal components are exposed to potentially corrosive outdoor environments. For example, cars, bridges, ships, and even outdoor structures often feature rust-proof paint to prevent rust’s detrimental effects.
Rust-proof paint is used on vehicle chassis, metal railings, outdoor furniture, and steel beams. Testing these paints for corrosion resistance is important because it helps evaluate their effectiveness over long periods and under different environmental conditions. By using the GenSalt tester, manufacturers can simulate years of exposure to harsh conditions within a short time. This ensures that paint formulations meet standards for protection and durability.

Anodized Metals
Anodizing, an electrochemical process, refines the surface properties of metals, especially aluminum. This process electrolytically increases the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the metal’s surface, yielding a finish that is far more durable than the base metal. The anodized layer is integrated with the underlying aluminum, providing exceptional durability and corrosion resistance.
The anodizing process is particularly valuable in industries like construction, electronics, and aerospace due to its enhancement of wear and corrosion resistance. Aluminum, known for its lightweight and robust characteristics, benefits significantly from anodizing, making it a preferred material in these sectors. Anodized aluminum finds widespread applications in products such as architectural details, kitchen appliances, electronic devices, and aerospace components.
One of the distinct advantages of anodized aluminum is its aesthetic enhancement. The anodized layer can be dyed in a wide range of colors, which not only increases the material’s visual appeal but also expands its use in design and decorative applications. This coloration process allows for significant customization in projects, making anodized metals a great choice for both functional and decorative uses.
Rust-Proof Grease
While not a material itself, rust-proof grease is a crucial application in combating corrosion, particularly in the metalworking and automotive industries. This type of grease acts as a barrier against moisture and other corrosive elements, providing long-term protection for metal parts during storage, transportation, and handling.
Rust-proof grease prevents corrosion in a number of settings, from industrial equipment to consumer products. It is especially relevant in environments where metal parts are exposed to harsh conditions. For example, it can be used in automotive underbodies, machinery spares, turbine blades, and even in the manufacturing and maintenance of ships and agricultural machinery.
Rust-proof grease creates a protective layer that insulates metal surfaces from humidity, salt, and acid rain. Its application is wide-ranging, as it can be used on everything from small fasteners to large mechanical components. Manufacturers often choose rust-proof grease for its ease of application and effectiveness in providing a durable protective coat that guarantees metal parts’ longevity and reliability over time.
Electroplated Coatings
Electroplated coatings are an integral part of modern manufacturing, providing a thin layer of protective metal over a substrate through an electrical deposition process. In this process, the substrate acts as the cathode within an electrolytic cell, and the coating metal serves as the anode. The application of electrical current causes the anode metal to dissolve and deposit onto the substrate, enhancing its corrosion resistance, wear resistance, aesthetic appeal, and electrical conductivity.
Electroplated coatings are essential to diverse industries, enhancing product functionality and lifespan. In the automotive sector, electroplated coatings are applied to components such as gears and bearings to withstand harsh operational conditions. In the electronics industry, coatings are used on connectors and switches to improve conductivity and durability.
Electroplating’s ability to apply precious metals like gold and silver to more common, cost-effective materials makes it invaluable. This not only provides a high-quality finish but does so in a financially viable manner, maintaining the desirable properties of more expensive materials while leveraging the economic benefits of less costly substrates.
Additional Applications of Corrosion Resistance Testing
Corrosion resistance testing extends far beyond the common fields of automotive, electronics, and aerospace. This type of testing is necessary for a number of lesser-discussed but equally important applications, making certain that all types of materials can withstand their environments.
In the field of architecture, corrosion resistance testing is crucial for materials used in iconic buildings and public infrastructure where material integrity impacts safety and aesthetics. For example, outdoor sculptures and monuments are tested to make sure they resist weathering and pollution, preserving cultural heritage.
In the energy sector, particularly in renewable energy installations like wind turbines and solar panels, materials must endure harsh environmental stresses. Corrosion testing ensures that wind turbine structural components can withstand marine or high-salt environments, crucial for offshore installations and that the frames holding solar panels remain robust under the scorching sun mixed with salty sea breezes.
Water treatment facilities use corrosion testing to select materials that resist harsh chemicals used in water purification processes. This testing confirms that pipes, tanks, and structural components can handle exposure to chlorine and other disinfectants without degrading.
In the manufacturing sector, tools and machinery exposed to corrosive industrial environments undergo rigorous testing.
Moreover, in the consumer products industry, items ranging from kitchen appliances to outdoor grills are tested to confirm that finishes and structural materials can resist stains, rust, and decay caused by exposure to food acids, high humidity, and unpredictable weather conditions.

Providing Durability and Safety Through Advanced Corrosion Testing
To summarize, the Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt by NextGen Material Testing Inc. plays an integral role in evaluating and verifying the durability and longevity of materials. This advanced testing unit is necessary when assessing how different coatings and materials can withstand harsh and corrosive environments. The Salt Spray Tester – GenSalt, with its robust construction capable of enduring high temperatures and its precision spray system, enables a thorough analysis of corrosion resistance.
This testing tool is designed with features like the Bernotte principle for uniform atomization and an adjustable dual-pressure system, which guarantees precise and reliable test results. These features make our salt spray tester an indispensable asset in industries requiring rigorous corrosion resistance testing, from architecture and renewable energy to automotive and consumer goods.
NextGen Material Testing Inc. stands as your dedicated material testing partner. Whether you require expert services or reliable testing equipment, we are here to help. Our commitment is to provide you with the tools and support needed to enhance your products’ quality and durability. If you have questions or need a consultation, do not hesitate to contact us directly or request an online quote. Our team is ready to help you tackle your material testing challenges and confirm that your products meet the highest standards of safety and performance.
